
There are a lot of love theories out there, but which one really describes love the best? It’s a big question, and the answer isn’t so simple. Here are nine different theories on love to help you make your choice.
Fatuous love
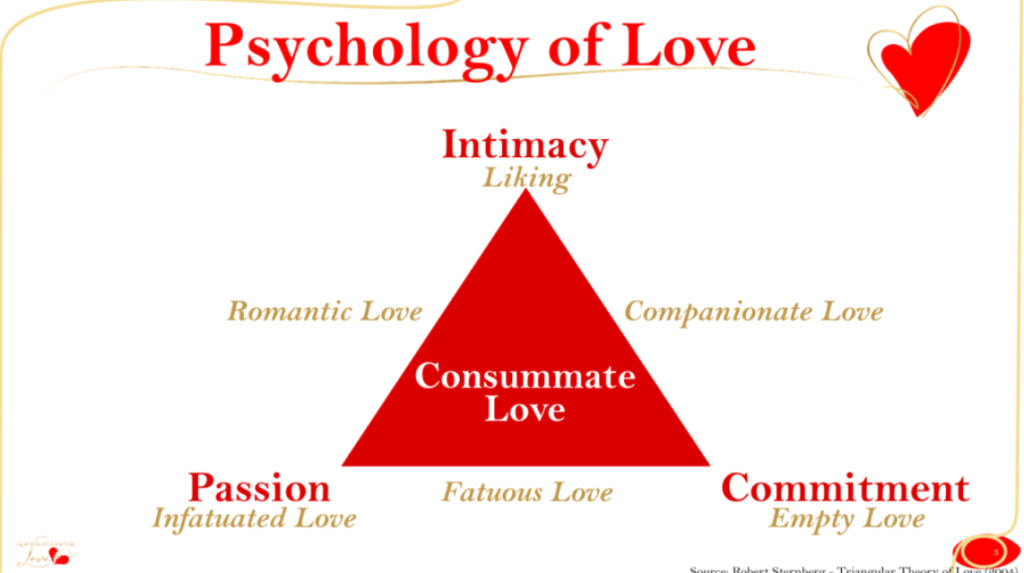
The triangular theory of love, created by world-famous psychologist Robert Sternberg, is a simple, yet highly effective means of defining and measuring the different kinds of love. It states that a relationship’s success depends on the balance of three factors: commitment, passion, and intimacy.
It is important to note that the triangular theory of love is not perfect. Some researchers have found that the relationship’s intensity may vary depending on the strength of each element.
While Sternberg’s triangular theory is useful in understanding the components of love, it doesn’t provide an easy way to tell if a relationship is headed for trouble. As a result, it’s not always accurate to measure love using the triangular model.
Nevertheless, it can be a useful tool to help you get closer to your sweetheart. Although it was published decades ago, it remains an effective method of measuring the different forms of love.
Infatuation is a whirlwind form of love. It is characterized by high arousal and intense physical attraction. These feelings can lead to disappointment and hurt.
Consummate love is a more complex form of love. It includes passion, commitment, and emotional intimacy. However, it is a little more difficult to maintain.
For example, compassion is a type of love. Compassionate love is sparked by different circumstances, but also includes the same idea of devotion.
Besides the Mere Exposure Effect and the triangular theory of love, there are some other theories to consider. The Mere Exposure Effect explains that people are attracted to things that they usually like. People like to have friends and relatives with similar interests.
In fact, a study in 1992 by Michele Acker and Mark Davis showed that college students who were attracted to their professors had higher scores on a test that measured commitment.
Mere exposure effect
The mere exposure effect is the result of repeated exposure to an item or situation. It is a cognitive psychology phenomenon, whereby people are more likely to like something after being exposed to it several times. Although it has been widely reported, its significance has not been fully explored.
It is generally thought to occur in situations where a familiar, but new, stimuli is presented. A more recent study suggests that the mere exposure effect can be seen when stimuli are perceived without awareness.
According to the Mere Exposure Effect, increased exposure to a novel stimulus increases the emotional intensity of a person. This may be due to the spatial pattern of the stimuli.
There have been many studies to explore this phenomenon. However, most of them do not make use of a randomized sample. In the simplest case, the mere exposure effect is observed when participants are exposed to a semblance of an imaginary polygon. When participants were asked to visualize the shape of this elusive geometrical construct, they did so.
Although the mere exposure effect is not always obvious, it is usually present when participants are given the same task in the rating and exposure phases of a single experiment. Interestingly, a paired t test suggested that mere exposure is indeed a thing.
While it’s true that the mere exposure effect has been investigated in numerous experimental settings, a meta-analysis of studies has not provided a consensus on the exact mechanism responsible for this mysterious effect. Other researchers have offered competing explanations, ranging from a change in evaluative stance to a reduced sensitivity to external stimuli.
For example, while the mere exposure effect has been found to exist in conditions where the stimulus is a color, it’s not often studied in those where the stimulus is a negative valenced stimulus such as a brand name.

Sternberg’s triangular theory
Whether you are a romantic soul or a lonely single, Sternberg’s triangular love theory in psychology is a great way to understand what love is and how to build a healthy, loving relationship. It focuses on intimacy, commitment, and passion.
Love is the all-consuming feeling that connects you to another person. While relationships can be complex and sometimes difficult, they are also the greatest gift of all. People have fallen in love and lived for love since time began.
There are many types of love, including lust, intimacy, and consummate love. Many people seek to experience consummate love. However, maintaining a relationship is a lot harder than achieving it.
The idea of a triangular theory of love comes from American Psychologist Robert Sternberg. He proposed it in the late 1980s. At that time, the dating landscape looked different. Dating apps hadn’t yet been invented, and people dated differently because they had fewer options.
During the 80’s, Sternberg’s theory was written while people dated differently. There was no Facebook, and cell phones were still pretty new. As a result, there was a lack of communication.



0